
To run the dig program on Mac OS X and Linux, follow these steps: We can also see that DNS server was used for the query. For example, the following output shows information for :įrom this, we can see that is currently pointing to IP address 93.184.216.119. At the > nslookup prompt, type the following commands: For example, to view the MX (mail exchanger) records for the domain, type nslookup at the command line.
To look up a different DNS record, you must enter interactive mode. For example, the following command performs a DNS lookup on the domain using an OpenDNS server (which has IP address 208.67.222.222):īy default, nslookup looks up the A record for a domain. To use a specific DNS server for the query, add the server name or IP address to the end of the command.Replace with the domain that you want to test:
#Mac terminal commands display dns windows#
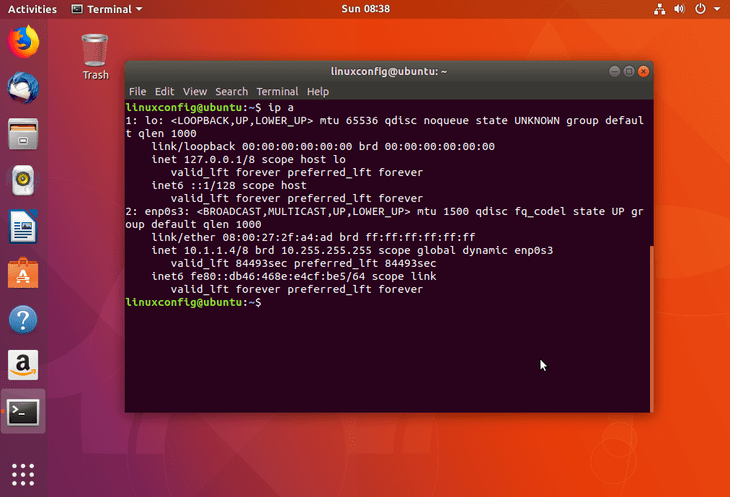
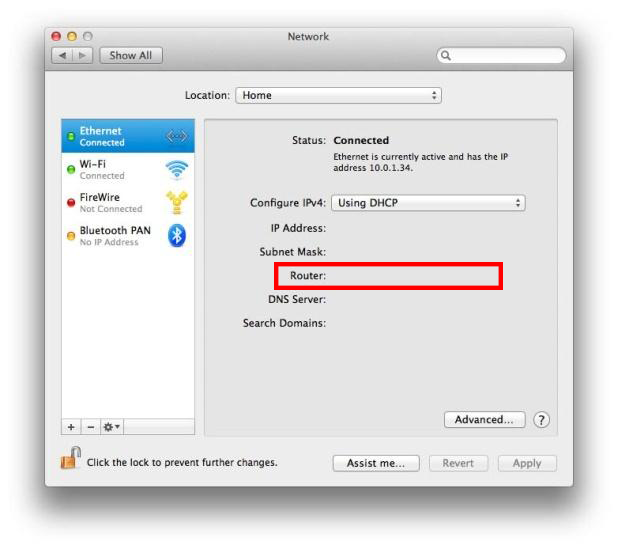
Microsoft Windows does not include the dig program. Follow the appropriate procedures below for your operating system. The exact steps to do this depend on your computer's operating system. While web-based tools are convenient and easy to use, it is often faster to use a command-line tool on your own system. Troubleshooting DNS with command-line toolsĭig (on Mac OS X and Linux) and nslookup (on Microsoft Windows) are the primary command-line tools for troubleshooting DNS issues. If the domain has an A record configured, dig displays the domain name and its associated IP address. The page displays the results from dig, as well as the actual dig command used. You can use the default name server, or select a specific DNS server, like OpenDNS or Google.

We will use –a to find out all records associated with. m set memory debugging flag (trace|record|usage)ģ. W specifies how long to wait for a reply R specifies number of retries for UDP packets N changes the number of dots allowed before root lookup is done l lists all hosts in a domain, using AXFR C compares SOA records on authoritative nameservers To get a list of host commands type host –help Open Terminal (Applications -> Utilities -> Terminal)Ģ. This is useful if you want to know certain information about a website or domain including geolocation of website hosted, check for email mx records, and validating a domain SPF record.ġ. You can use Terminalin Mac to lookup any and all associated host recordsfor any domain name on the Internet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
